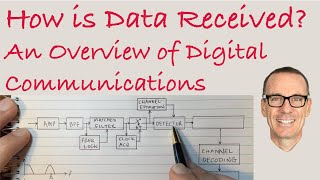
How is Data Received? An Overview of Digital Communications
Explains how Digital Communication Receivers work to turn the received waveform back into data (ones and zeros). Discusses the basic fundamental situation for wireless and mobile communications, and for Ethernet, digital subscriber lines (DSL), and optical fibres.
This is Part 2 of an overall system overview. The Transmitter was covered in Part 1 "How is Data Sent? An Overview of Digital Communications" https://youtu.be/MAddbFfCsIo
* Note that I made a minor error in showing the Detector before the Equaliser. What I had intended to do was to show them as a single block, since they are most often implemented as a single function (but I was trying to think of too many things at once). If they are implemented separately, then the equaliser comes first. I have fixed it on the Summary Sheet.
Other related videos: (see http://iaincollings.com)
• What is a Matched Filter? https://youtu.be/Ci-EjiMJo3I
• What is a Constellation Diagram? https://youtu.be/kfJeL4LQ43s
• What is Intersymbol Interference ISI? https://youtu.be/I087FUvW2ys
• How are Different Equalization Methods Related? (DFE, ZF, MMSE, Viterbi, OFDM) https://youtu.be/hYNwTTWrp48
• How are Data Rate and Bandwidth Related? https://youtu.be/ZBSvMbO0mPQ
• How are Throughput, Bandwidth, and Data Rate Related? https://youtu.be/IY6fDYwC2fU
• How are Bit Error Rate (BER) and Symbol Error Rate (SER) Related? https://youtu.be/du-sExIUV-Y
• What are Channel Capacity and Code Rate? https://youtu.be/P0WY96WBUyA
• What is Entropy? and its relation to Compression https://youtu.be/FlaJPxP8sd8
• What is Pulse Shaping and the Square Root Raised Cosine? https://youtu.be/Qe8NQx4ibE8
Full Categorised list of videos and PDF Summary Sheets: http://iaincollings.com
.