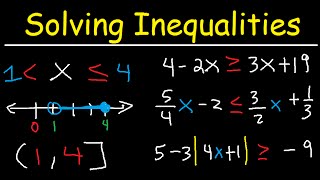Interval Notation Explained - The Basics You NEED to Know!
Today, we're covering how to express a solution in interval notation, which is common when solving an inequality.
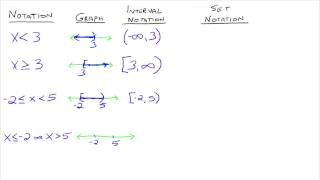
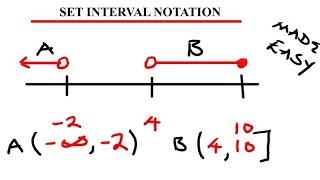
The interval notation has a few components - parenthesis, brackets, and the number (or infinity), separated by a comma. Parenthesis are used when the inequality symbol has either a "less than" or "greater than" sign, which is represented with an open circle on a number line, indicating that the number itself is not included. A bracket is used when the symbol is "greater than or equal to," or "less than or equal to." Infinity will always have a parenthesis, since we cannot include it - it is a concept, not an actual number.
We'll review several examples you need to know, including the union of two sets, represented by a "U," which joins two sets together, as well as the intersection, represented by an upside down "U," which only looks for the overlap between sets.